https://doi.org/10.1140/epjqt/s40507-024-00234-0
Research
A quantum moving target segmentation algorithm for grayscale video based on background difference method
1
School of Information Science and Engineering, Southeast University, 211189, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
2
State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves, Southeast University, 210096, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
3
Quantum Information Center, Southeast University, 210096, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
4
National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory, Southeast University, 210096, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
5
College of Artificial Intelligence, Nanjing Tech University, 211800, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
6
School of Software, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 210044, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
7
Purple Mountain Laboratories, 211111, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
Received:
30
January
2024
Accepted:
14
March
2024
Published online:
3
April
2024
The classical moving target segmentation (MTS) algorithm in a video can segment the moving targets out by calculating frame by frame, but the algorithm encounters a real-time problem as the data increases. Recently, the benefits of quantum computing in video processing have been demonstrated, but it is still scarce for MTS. In this paper, a quantum moving target segmentation algorithm for grayscale video based on background difference method is proposed, which can simultaneously model the background of all frames and perform background difference to segment the moving targets. In addition, a feasible quantum subtractor is designed to perform the background difference operation. Then, several quantum units, including quantum cyclic shift transformation, quantum background modeling, quantum background difference, and quantum binarization, are designed in detail to establish the complete quantum circuit. For a video containing  frames (every frame is a
frames (every frame is a  image with q grayscale levels), the complexity of our algorithm is O
image with q grayscale levels), the complexity of our algorithm is O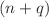 . This is an exponential speedup over the classical algorithm and also outperforms the existing quantum algorithms. Finally, the experiment on IBM Q demonstrates the feasibility of our algorithm in this noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) era.
. This is an exponential speedup over the classical algorithm and also outperforms the existing quantum algorithms. Finally, the experiment on IBM Q demonstrates the feasibility of our algorithm in this noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) era.
Key words: Quantum video processing / QVNEQR / Moving target segmentation / Background difference / IBM Q
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




